Table of Contents
What do you think of when someone mentions NO boosters? Many of you probably know that these pre-workouts are sought after by those who want to pump up their muscles with energy and get a jump start on world-class athletic performance. This is because these substances help bring more oxygen and nutrients to the muscles. Arginine is the leader in this regard, and today you can learn more about its effects on athletic performance and overall health.
In this article you will read about the effect of arginine on these specific areas:
What is arginine?
Arginine is an amino acid commonly used as a building material for the formation of body proteins. It is a semi-essential amino acid, which means that in most cases you can produce it yourself and do not need to ingest it. However, under certain conditions this is not enough, so it is necessary to supplement it in larger quantities externally. This is for example during periods of growth or serious illness or injury, when the body has a higher requirement for this amino acid.
Arginine can therefore be synthesised by the body itself, yet roughly 80% comes from your diet or the breakdown of body proteins. Its production occurs in the kidneys, liver and brain. Interestingly, it is produced in the biochemical urea cycle, which is used to remove a toxic waste product of metabolism, called ammonia, from the body.
The main benefit of arginine is its participation in the formation of nitric oxide. This is needed to control blood flow in the body, the function of cellular power plants (mitochondria) or the transfer of information between cells. In addition, the body uses it as a starting substance for the formation of other amino acids such as citrulline or ornithine. [12,15]
To learn more about amino acids, read our article Amino Acids: Breakdowns, Functions in the Body, Effects on Athletic Performance, and the Best Sources.

How does arginine work?
Arginine can be incorporated into muscle proteins or used for energy, which is typical of all amino acids. However, it also has a specific role, namely the formation of the aforementioned nitric oxide (NO), which is linked to many of its positive effects on the body.
The enzyme NOS (nitric oxide synthase) is formed in the vascular walls. Its task is to bind arginine to itself and convert it into nitric oxide and citrulline, which can be converted back into arginine. The NO formed is the main active substance responsible for dilating blood vessels (vasodilation) and relaxing them, which is important for many processes in the body. [8]
Nitric oxide also has other important tasks in the body, such as helping to destroy harmful bacteria or aiding the activity of immune cells.
Some other important substances are also formed from arginine. These include the already mentioned citrulline, which is also used as a nutritional supplement because it can also increase NO levels in the body. Arginine also serves, together with glycine and methionine, as a base for the formation of creatine, which is produced primarily in the liver and kidneys and is important for energy production. [6]
You can learn more about citrulline in our article L-citrulline and All You Need to Know About It.
You might be interested in these products:
What are the health benefits of arginine?
1. Affects sports performance
Arginine is known as a nutritional supplement that can help energise the muscles to perform better. However, research shows that it can have several positive effects that can take sport performance to the next level.
- It helps to improve blood flow in the body, thanks to the aforementioned nitric oxide it produces.
- This results in more efficient oxygenation and nutrient delivery to the muscles. This is because dilated blood vessels, through which more blood flows, can deliver more oxygen and nutrients to muscle tissue for maximum sports performance.
- This is also linked to its effect on increasing VO2 max, which has been shown in some studies. This value speaks about the maximum amount of oxygen the muscles are able to use. The higher it is, the higher the physical performance. The highest values are commonly achieved by the best endurance athletes, such as cross-country skiers or marathon runners. [7]
- It can help to improve muscle contraction and thus lead to more intense performance. [13]
- Thanks to nitric oxide, muscles may be more resistant to fatigue and recover better.
- It also has an effect on strength, intensity and explosiveness, thanks to its role in the formation of creatine. [13]
- Arginine also helps with the removal of lactate more rapidly. This is produced in the muscles during intense activity when they do not get enough oxygen (for example during sprinting, strength training, etc.). It manifests itself in the characteristic burning of the muscles, which forces you to slow down or take a break. Studies suggest that arginine may promote the breakdown of lactate during activity. [11]
- In research, it has been shown to promote the production of growth hormone and testosterone at the same time. These play an important role in muscle growth, strength and recovery. [13]
- Thanks to these effects, arginine may be useful in anaerobic (strength training, weightlifting, sprinting, etc.) and endurance sports (running, cycling, swimming, triathlon, etc.). [13]

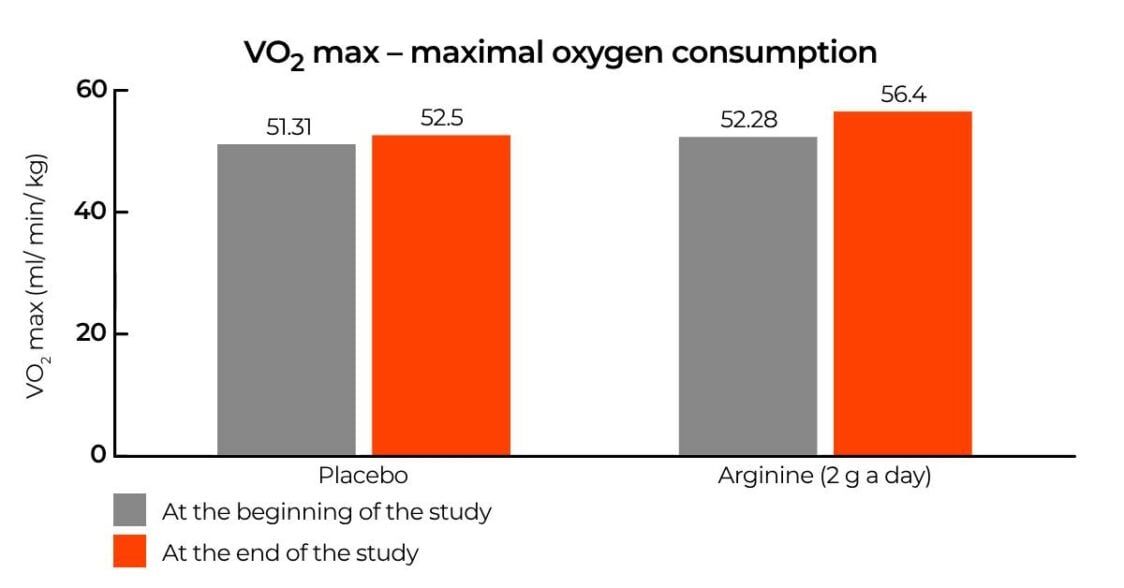
How does science see it? Effect of arginine on VO2 max
The role of arginine in sports performance was also shown in research that followed 52 football players. They underwent football training four times a week for 45 days and took either 2 g of arginine a day or a placebo in the form of maltodextrin. Before and after their training program, they underwent the so-called Harvard Step Test, where they climbed a 50 cm step for 50 minutes at a rate of 30 steps per minute. Before and after both tests they were measured for VO2 max.
The arginine group was shown to have a higher VO2 max than the placebo group, with an average increase of 4 ml/min/kg. At first glance this may seem like a small difference, but in reality an increase of just 1-2 units can lead to a significant difference in performance. [7]
2. Positive effect on cardiovascular health
The benefits of arginine on cardiovascular health are fairly well known, as the nitric oxide that forms from this amino acid has a direct effect on your blood vessels. As we have already mentioned, NO is an essential molecule for vasodilation, or the expansion of blood vessels and their relaxation. How can this be beneficial?
- It can help with lowering blood pressure. When blood pressure is high, the blood vessels are constricted and tight. The aim of treating hypertension is thus, among other things, to widen these vessels and improve blood flow, which arginine can help with. [6]
- Studies also show benefits in those with ischaemic problems. If a person suffers from ischaemia (blood clotting) of the heart muscle, dilating the blood vessels with NO created from arginine could help reduce symptoms (chest discomfort, burning sensations, chest pain – angina and more). [6]
- It could also have an effect on endothelial dysfunction. This is damage to the blood vessel wall typical of atherosclerosis (‘hardening of the blood vessels’), where blood vessels narrow and fat and other blood components accumulate inside the wall. The dilation of blood vessels by nitric oxide could improve this condition. In addition, there is also talk of possible anti-inflammatory effects that may help fight inflammation in such a damaged blood vessel wall. [6]
Discover our bestsellers:
How does science see it? The effect of arginine on blood pressure
The best-studied effect of NO on cardiovascular health is its effect on blood pressure levels. This was also shown in a study that followed 75 women for two weeks. These women were divided into three groups, with one consisting of younger healthy women aged 20 to 30, the second consisting of older healthy women, and the third consisting of women with type 2 diabetes. Some of the women in the first two groups may have had slightly elevated blood pressure (a blood pressure of 120/80 mmHg is considered optimal, but a healthy value may be individual to each person).
All participants took 5 g of arginine daily for two weeks. The researchers measured their systolic and diastolic blood pressure at the beginning and end of each follow-up. In the end, it appeared that significant reductions in both systolic and diastolic pressure occurred in the older healthy women and in the women with diabetes. [1]
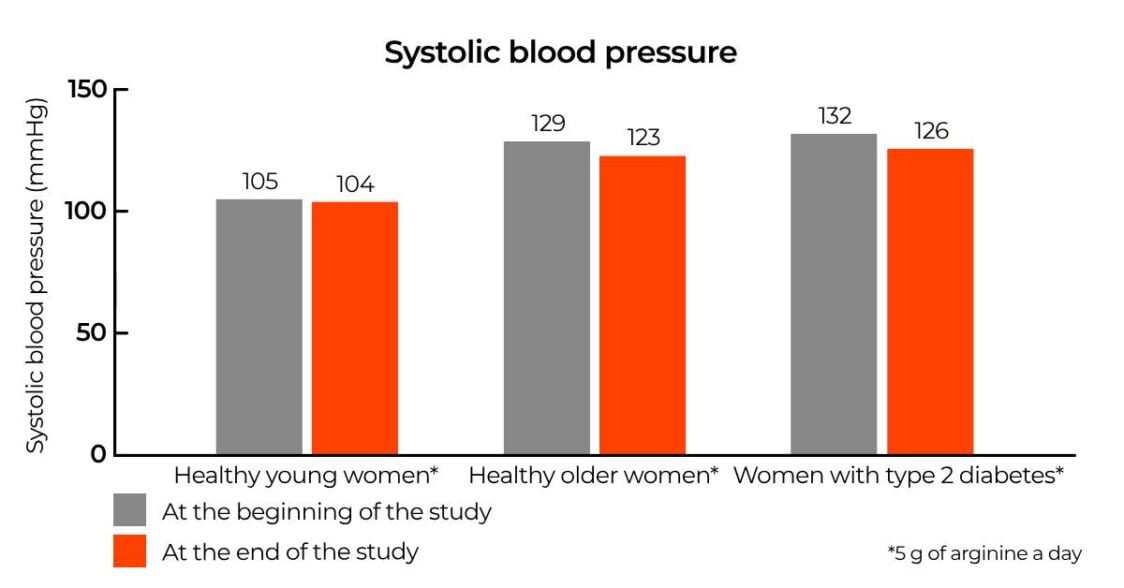
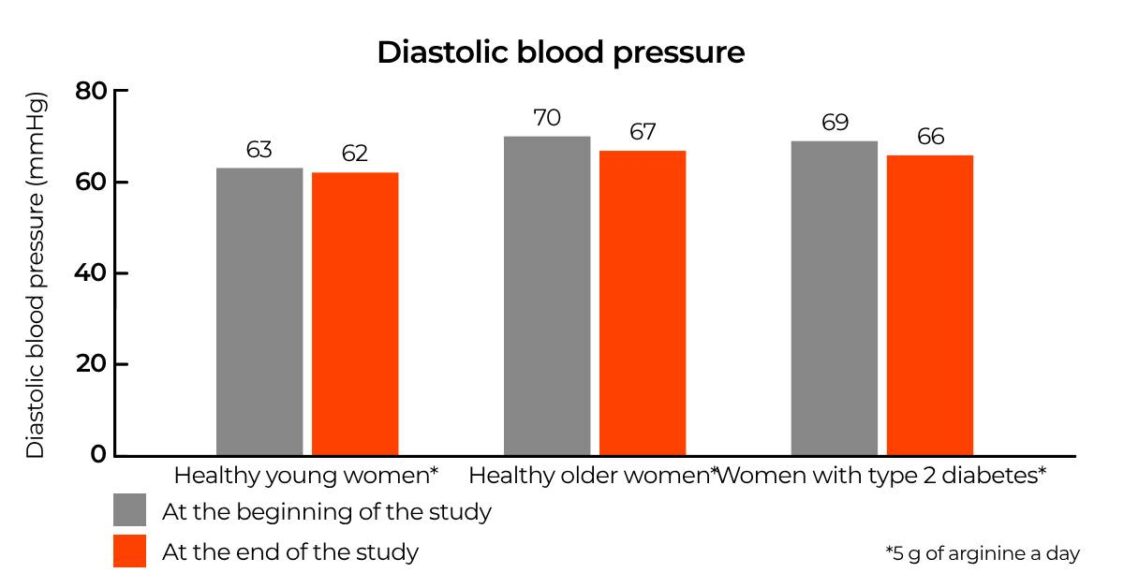
Of course, arginine cannot be considered a cure for high blood pressure, but for some it can be part of their treatment when trying to get this health parameter under control. However, it is always important to consult a doctor in such cases.
3. Has an effect on the immune system
According to several studies, arginine also plays an important role in many immune functions, again mainly through the production of nitric oxide.
- It apparently plays a role in the production of T-cells, which are white blood cells essential in immune reactions. Thus, arginine could, for example, help fight infection.
- There is also talk about the antimicrobial effects of arginine, which in practice would theoretically mean that arginine would have the ability to help destroy harmful pathogens.
- Studies have also reported its importance in the production of cytokines. These are used by your body to fight inflammation. Thus, it seems that arginine could have anti-inflammatory effects.
For more tips on how you can boost your immunity, check out 15 Ways to Boost Your Immune System and Protect Your Health.
4. May affect the action of insulin and blood sugar levels
Research suggests that arginine could also help with insulin function and blood sugar regulation (glycaemia). This is because insulin helps move sugar from the blood (glucose) into the cells where it is converted into energy. This hormone thus directly affects blood sugar levels.
Apparently, nitric oxide can have a protective effect on the beta cells of the pancreas, the cells that produce insulin. Moreover, its role in how the body responds to this hormone is gradually being revealed. In other words, it could improve the sensitivity of cells to insulin. [12,16]
These promising effects of arginine may be important for those suffering from type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance. In both cases, insulin action is insufficient and, among other things, results in higher than optimal blood sugar levels. The promising effect of arginine, specifically the nitric oxide it produces, is also indicated by a study in which researchers concluded that people with diabetes have lower NO levels. [2,16]
How does science see it? The effect of arginine on blood sugar levels
The link between arginine and blood sugar levels was also shown in a study of 33 people with obesity and type 2 diabetes. The participants followed a low-calorie diet and a prescribed training programme for 21 days, with half of them taking 8.3 g of arginine daily and the rest receiving a placebo. Their blood sugar levels were measured before, during and after the programme. It showed that fasting glucose dropped significantly more in those taking arginine than in those taking the placebo. [5]
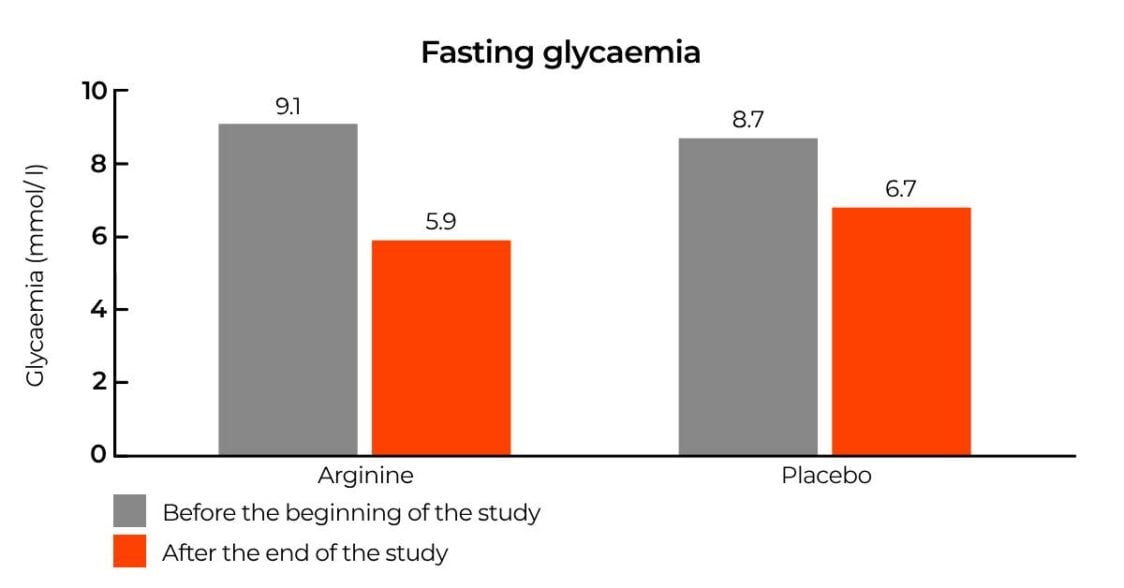
Although glycaemia fell without the participants taking medication, we cannot be certain that arginine could be considered a cure for diabetes. Diet and a training program played a role in this case, which are essential on the road to improving glycaemia. Therefore, it is always ideal to consult experts regarding the use of medication, proper diet and a training program before considering nutritional supplements.

5. It has an effect on erectile dysfunction and sexual health
Another benefit of arginine is its effect on male sexual health. In fact, according to research conducted to date, it appears to help with erectile dysfunction. Erection is accompanied by dilation of blood vessels (vasodilation) and their relaxation, which is influenced by nitric oxide, which is produced from arginine. [10]
Not only that, arginine is the basis of most erection supplements. Its effect is confirmed by a meta-analysis, which showed that arginine had a significant effect on improving erections in men with erectile dysfunction, both as a stand-alone supplement but also in combination with other substances (e.g. yohimbine or ornithine). In case you want to take arginine in order to address a specific health problem, you would do well to consult with a doctor for advice as well. [10]
If you’re wondering what other substances and nutrients can help support men’s health, check out our article Men and Nutrition: The Most Important Vitamins and Minerals for Health, Testosterone, and Performance.
6. Uses in medicine
Arginine is commonly used in intensive care medicine when its reserves in the body are significantly depleted.
These include injuries or serious infections of varying severity. This is when the need for arginine increases significantly and it is important to supplement it, as a serious deficiency can lead to, for example, impaired immune function or disturbances in blood circulation. [9]
7. In what other areas is arginine being researched?
The benefits of arginine that we’ve covered so far are among the most researched. However, there are other areas of health where research shows promising potential for arginine.
- This is, for example, a possible effect on accelerating healing.
- The antioxidant properties of arginine have also been discovered. It appears to support the function of glutathione, one of the most important antioxidant systems in the body that fights oxidative stress. [4]
- Nitric oxide, and thus its precursor arginine, most likely plays an important role in the development of the nervous system. [16]
- In combination with lysine, it is said to have an effect on reducing anxiety. [16]
- It can also be considered as an anti-ageing or healthy ageing supplement because its benefits can contribute to healthy ageing. [3]
Where in food can you find arginine?
The sources of arginine are mainly protein-rich foods. These include meat, dairy, legumes and nuts. Moreover, watermelon, oats or chocolate are also rich in arginine.
How much arginine do some foods contain on average?
| Food source | Arginine content (g/100) |
|---|---|
| chicken meat | 1.5 |
| beef | 1.1 |
| salmon | 1.2 |
| eggs | 0.8 |
| white yoghurt | 0.16 |
| edam cheese | 0.96 |
| watermelon | 0.06 |
| pumpkin seeds | 5.4 |
| oatmeal | 0.85 |
What side effects does arginine have?
If you take arginine as recommended, you don’t have to worry about side effects. However, if you overdo it, you may experience particularly unpleasant digestive problems. For example, vomiting, diarrhoea or nausea. Headaches or low blood pressure, for example, have also been documented in connection with arginine. To avoid these side effects, it is recommended to take no more than 20-30 g of arginine per day. [12]
Side effects may also occur in combination with certain medications. For example, if you are taking medication to lower your blood pressure, in conjunction with arginine your blood pressure could drop too much, which can be dangerous. Therefore, if you are taking any medication, it is advisable to consult your doctor before taking arginine.
Forms of arginine
Arginine is commonly encountered in two forms, namely as L-arginine or arginine alpha-ketoglutarate.
- L-arginine is a form of the amino acid arginine that is naturally found in foods and in the human body. This form is also used in medicine, for example in the treatment of cardiac problems or the aforementioned extensive injuries.
- Arginine alpha-ketoglutarate (AAKG) is a combination of the amino acid l-arginine and the salt of glutaric acid. Its advantage is improved absorption and gradual release of arginine into the blood. It is more often found in supplements for athletes who, in addition to supplying muscles with oxygen and nutrients, also aim to grow muscle mass.
How to take arginine?
There is no recommended dosing protocol for taking arginine, but the standard recommendation is to take 3-6 g of arginine at a time. This is an amount that has been shown in studies to be effective while being of low risk for digestive problems. To maintain higher blood levels of arginine, three smaller doses can be taken daily, up to a total of 15-18 g of arginine/daily. [12]
- For maximum support of sport performance, it is advisable to supplement with arginine 30 – 90 minutes before activity. The specific amount depends on tolerance. It is therefore advisable to start at a lower dose (e.g. 2 g) and increase as necessary.
- To support health and maintain optimal levels of arginine in the body, it is adequate to take lower doses within the normally recommended intake at any time of the day.
Arginine can be taken in tablets or powder. The effect of both of them is comparable, so it depends only on your preference which of the forms you choose.
What to combine arginine with?
Arginine can be combined with other substances that have similar effects on health and sports performance. Thus, they can complement each other and you can get more out of their combination than if you took them separately. Which substances are important to consider?
- Although citrulline is formed from arginine, it works the other way around. If you supplement citrulline, it can convert to arginine and lead to the formation of nitric oxide. Studies have even suggested that citrulline can increase the level of arginine in the body more effectively compared to arginine alone.
- Beetroot powder or other concentrated forms of this vegetable are high in nitrates, which are converted to nitric oxide in the body. It can thus be a good companion with arginine and its effects.
- Taurine is commonly included in pre-workout mixes and energy drinks. It may be a suitable supplement to take with arginine prior to sporting performance.
- Ornitine, like arginine, is associated with normal muscle activity and thus may be a good supplement for athletes.
- Beta-alanine can be useful in combination with arginine during a demanding training program when you want to deliver the best possible anaerobic performance.
- Resveratrol is used in the care of the cardiovascular system and thus can form a suitable combination with arginine, which is also known for its positive effect on the heart and blood vessels. You can take it alone or in combination with other substances with antioxidant effects.

What should you remember?
Arginine is one of the supplements that are used to support sports performance. However, in addition, it has several other interesting health effects. For example, it is part of the immune response and may be involved in lowering blood pressure or blood sugar. Behind all these effects is probably nitric oxide, which is formed from arginine and is involved in the dilation and relaxation of blood vessels. While arginine still requires more research to know exactly how it works, we can already see that it is a promising supplement with many interesting benefits.
If you found this article interesting and learnt something new, feel free to share it.
[1] COSTA, G. et al. Oral L-Arginine (5 g/day) for 14 Days Improves Microcirculatory Function in Healthy Young Women and Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Elderly Women. – https://karger.com/jvr/article/59/1/24/824329/Oral-L-Arginine-5-g-day-for-14-Days-Improves
[2] FORZANO, I. et al. L-Arginine in diabetes: clinical and preclinical evidence. – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10114382/
[3] GAD, M.Z. Anti-aging effects of l-arginine. – https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2090123210000573
[4] LIANG, M. et al. l-Arginine induces antioxidant response to prevent oxidative stress via stimulation of glutathione synthesis and activation of Nrf2 pathway. – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29577948/
[5] LUCOTTI, P. et al. Beneficial effects of a long-term oral l-arginine treatment added to a hypocaloric diet and exercise training program in obese, insulin-resistant type 2 diabetic patients. – https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpendo.00002.2006
[6] MCRAE, M.P. Therapeutic Benefits of l-Arginine: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses. – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5021928/
[7] PAHLAVANI, N. et al. The effect of l-arginine supplementation on body composition and performance in male athletes: a double-blinded randomized clinical trial. – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28120856/
[8] PARK, H.-Y. et al. Dietary Arginine and Citrulline Supplements for Cardiovascular Health and Athletic Performance: A Narrative Review. – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10005484/
[9] PATEL, J.J. et al. When Is It Appropriate to Use Arginine in Critical Illness? – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1177/0884533616652576
[10] RHIM, H.C. et al. The Potential Role of Arginine Supplements on Erectile Dysfunction: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30770070/
[11] SCHAEFER, A. et al. L-arginine reduces exercise-induced increase in plasma lactate and ammonia. – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12215958/
[12] SOLOMON, T. Arginine Research Analysis. – https://examine.com/supplements/arginine/
[13] VIRIBAY, A. et al. Effects of Arginine Supplementation on Athletic Performance Based on Energy Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7282262/
[14] FoodData Central. – https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173757/nutrients
[15] L-arginine Uses, Benefits & Dosage - Drugs.com Herbal Database. – https://www.drugs.com/npp/l-arginine.html
[16] Research Breakdown on Arginine - Examine. – https://examine.com/supplements/arginine/research/#8lrKB29-cardiovascular-health


Add a comment